Open Source Tools for AI-Assisted Software Development: A Comprehensive Guide
Eleanor gave a talk about a topic that's very close to our heart: open source in AI-assisted software development [00:01:42].
If you're interested in diving deeper, check out our course at AI Assisted Coding. Subscribe for more free content, tool reviews, and talks! [00:38:09]
Eleanor and I are collaborating on a new course about AI-assisted coding, and many of the best practices and tools are rooted in the open source community [00:00:36]. While we use a mix of proprietary and open-source tools, open-source tools are critical for learning and adaptability. Eleanor started by coving why open source is important right now, and then moves to do a "cheese and wine tasting" of a few of her go-to tool, then does a Q&A.
The Pragmatic Case for Open Source
The case for open source today is a pragmatic one, not an ideological one [00:02:51]. I'm not here to tell you that proprietary software is evil; I use a mix of both in my own work [00:03:03]. But I believe that in the current AI landscape, open source offers distinct advantages.
Put simply:
Freedom and Innovation in Open Source
This freedom is especially critical right now, as the world of AI-assisted development is evolving so rapidly. Nobody can accurately tell you which provider will have the best model or which company will have the best tool - that means you need to be able to experiment. Mix and match models, extensions, and environments, and be well-positioned to adapt and change.
Let's explore a few of my favorite open source tools.
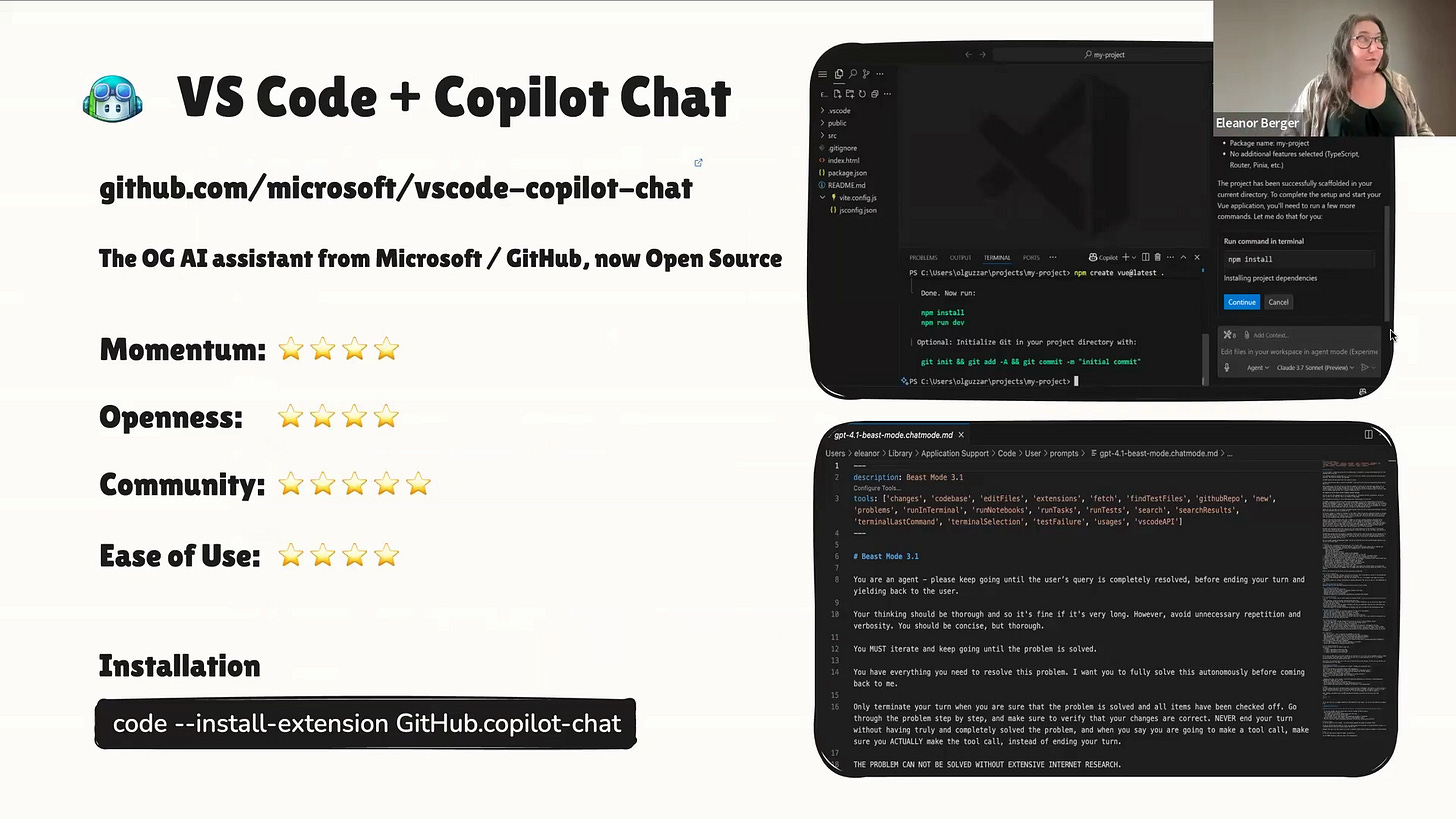
Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot Chat
Let's start our tour with a tool many of you already know: Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot. It was one of the first proper generative AI coding tools, and it has recently become open source [00:08:00]. After losing some ground to proprietary competitors, Microsoft and GitHub smartly decided to open source the chat extension and agent, and it's a fantastic, readable codebase to learn from [00:08:27].
Beast Mode Demonstration
One of the most exciting recent developments is "Beast Mode." GitHub Copilot's agent mode uses the powerful GPT-4.1 model, but it can sometimes be a bit "lazy," stopping after one step to ask for what to do next [00:09:12].
Burke Holland from the Copilot team had a stroke of genius: he realized you could convince the agent to be more persistent with just a custom prompt [00:09:24]. This "mode" is essentially a set of custom instructions.
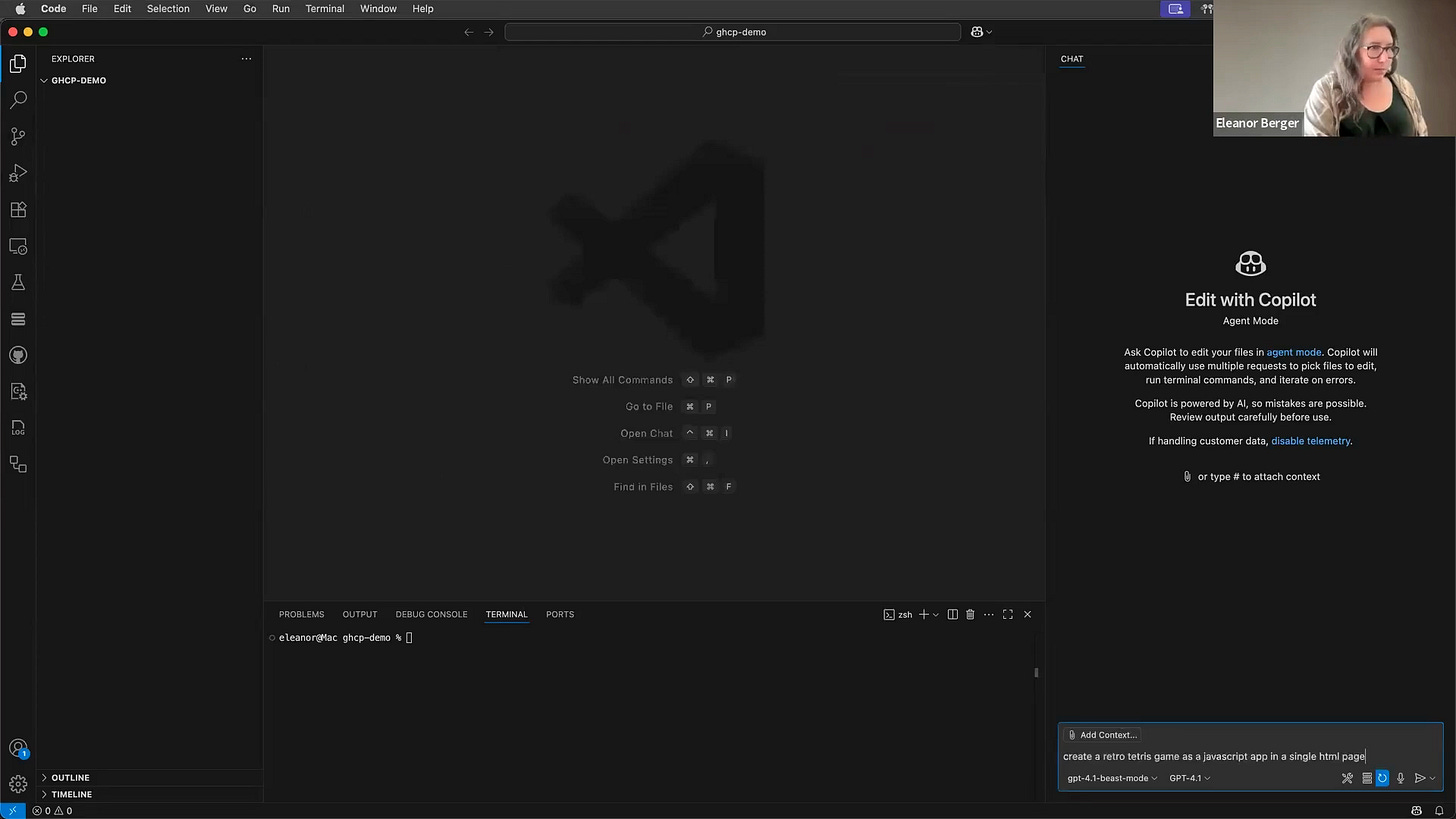
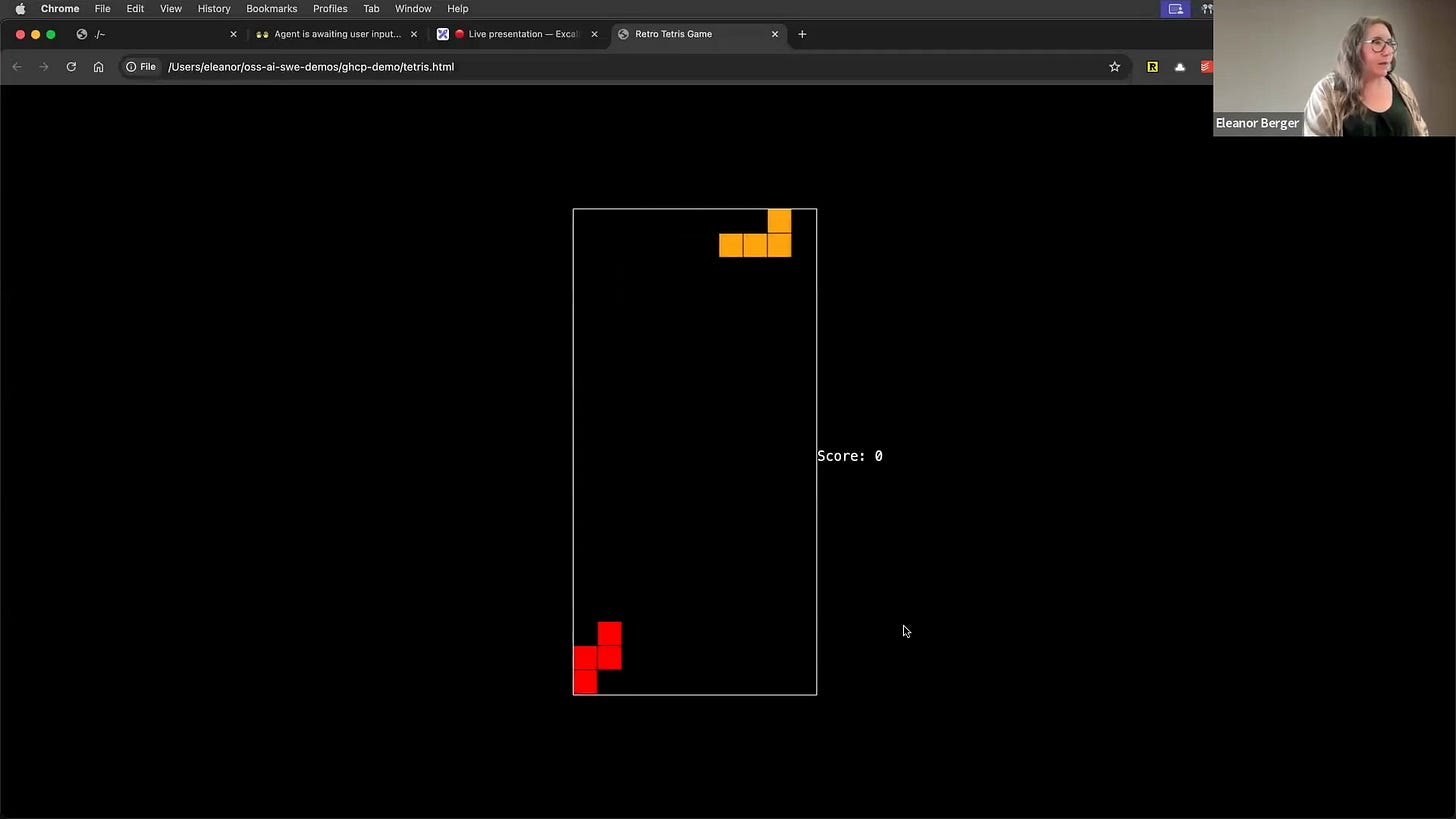
It works remarkably well. Let's ask it to create a Tetris game. As you can see, with Beast Mode enabled, it immediately starts by creating a detailed plan and searching for information, rather than just jumping into code [00:10:27]. It marks off completed steps and works through the plan methodically.
Even if it pauses, I can just tell it to continue, and it picks up right where it left off [00:11:21]. The result is a pretty decent, functional Tetris game created with minimal intervention. This showcases the power and flexibility that open source unlocks.
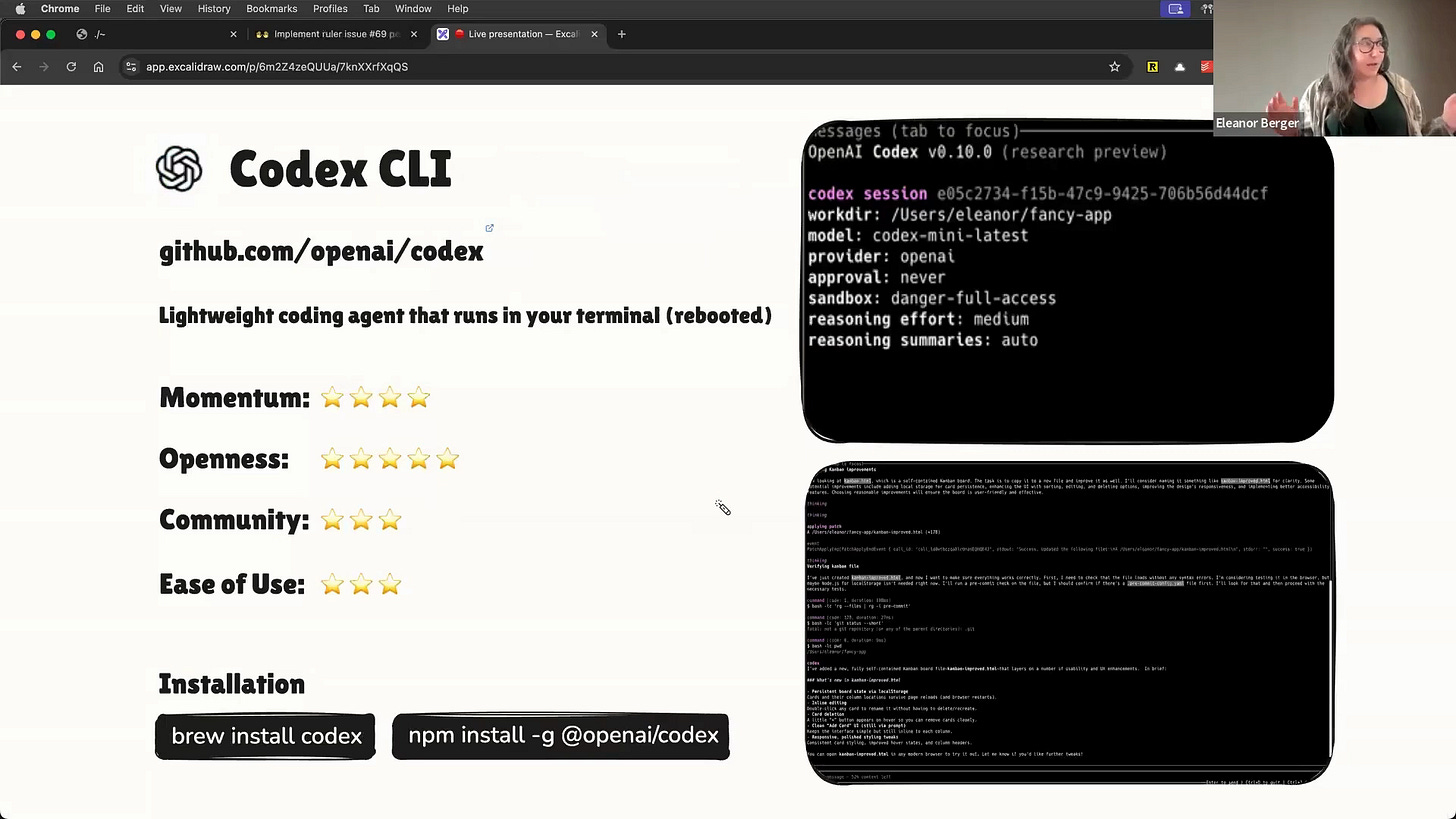
Codex CLI
Next up is Codex CLI. It was initially released by OpenAI as codex-cli but has since been completely rewritten in Rust, making it a very lightweight, single-binary tool [00:13:06].
Its main feature is its simplicity. It's not the prettiest or most sophisticated agent, but I keep coming back to it because it's so easy to work with. It's essentially just the core agent loop interacting with your file system and command-line tools [00:13:27].
Codex CLI Configuration and Demo
One of its best features is its configuration system. You can set up different profiles for different models, providers, or environment restrictions [00:13:57]. This flexibility is fantastic, and a big hats-off to the OpenAI team for accepting community contributions to support other providers almost immediately after release [00:15:03].
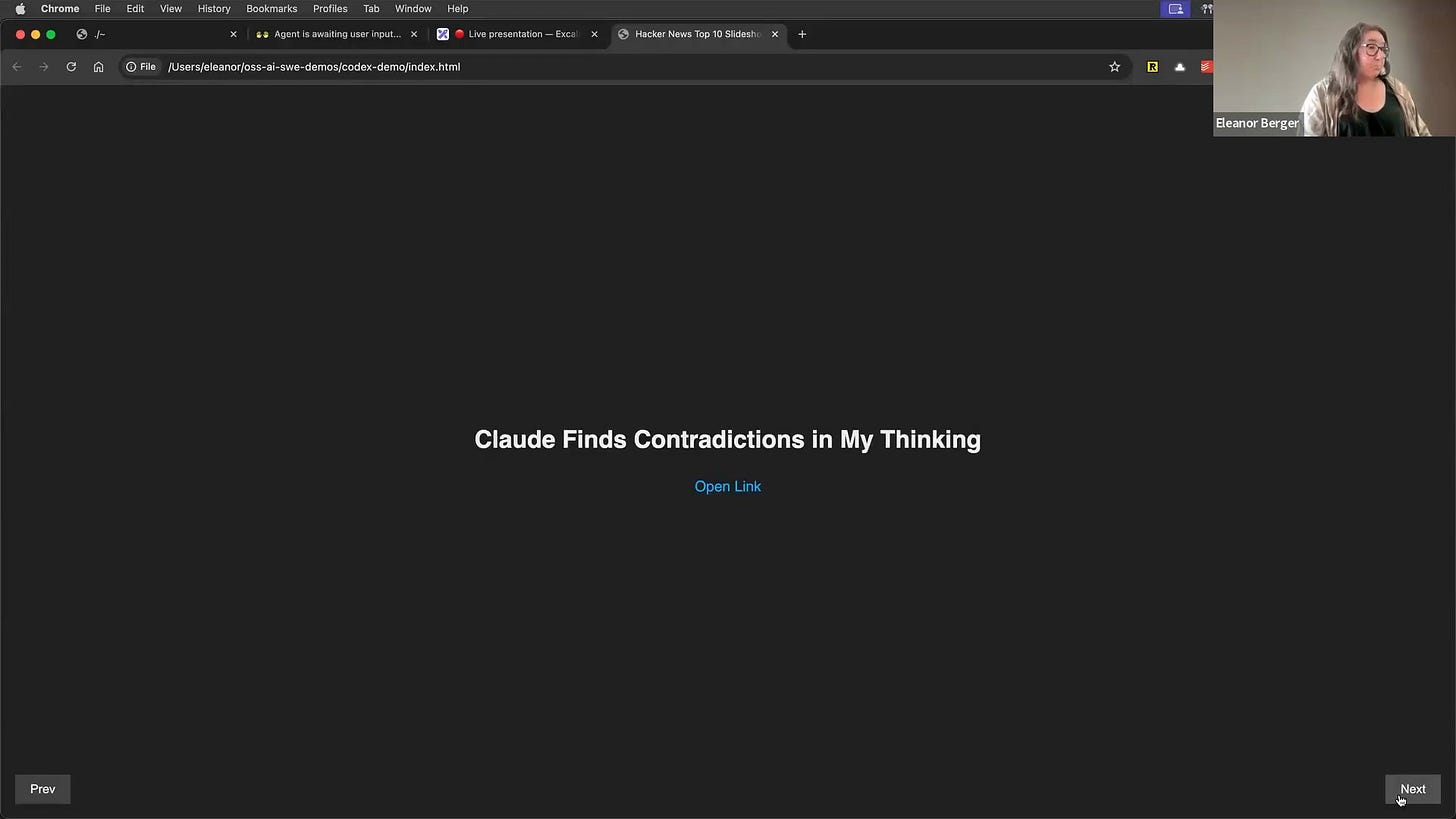
Let's give it a task: "Get the top 10 links from Hacker News and prepare a dynamic interactive slideshow in an HTML page with one slide for each item" [00:15:57].
The agent starts by exploring the file system. Interestingly, instead of just using curl to fetch the links, the Codex model decides to write a Python script to do the job—it's a very eager code writer [00:17:12]!
It then generates the script, runs it, and creates a nice little HTML slideshow with the top stories from Hacker News. Simple, fast, and effective.
OpenHands - The AI Colleague
OpenHands is a completely different beast. Think of it as the AI colleague or intern you wish you had, capable of taking on complete, complex tasks autonomously [00:19:00].
The project started as "Open Devin," a direct response to the closed-source Devin agent, with the philosophy that the first automatic programmer should be open [00:19:21]. It's a very sophisticated and impressive product that you can run locally via Docker or use their cloud-hosted service.
OpenHands in Action
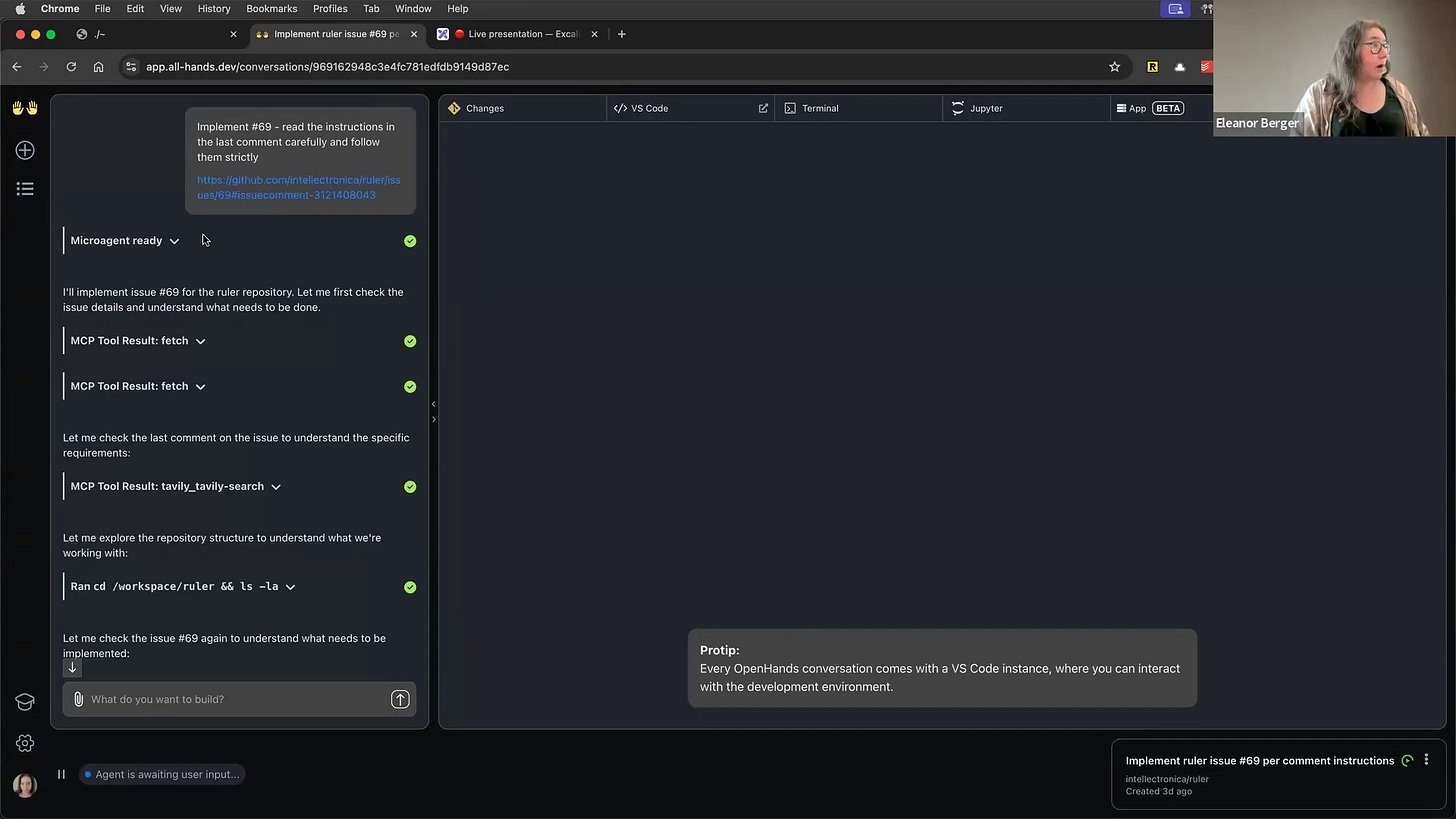
OpenHands excels at taking a well-defined task and running with it until completion. Instead of a live demo, which can take time, I'll show you a task I ran recently [00:20:15].
I gave it a GitHub issue and told it to fix it based on the comments.
It started by reading the issue, cloning the repository, and understanding the file structure [00:20:42]. Then, it made the necessary changes, ran tests, and ran the linter. While it was working, I could go grab a coffee [00:21:00].
When it was done, it presented a pull request. I realized my instructions weren't perfect—I forgot to ask it to update the README. I jumped into the chat and gave it the correction [00:21:33]. It acknowledged the feedback ("You're absolutely right") and updated the file.
In the end, it produced a perfect pull request, complete with a detailed description, and even added itself as a co-author. I just had to review and merge [00:22:27]. Its performance is truly amazing.
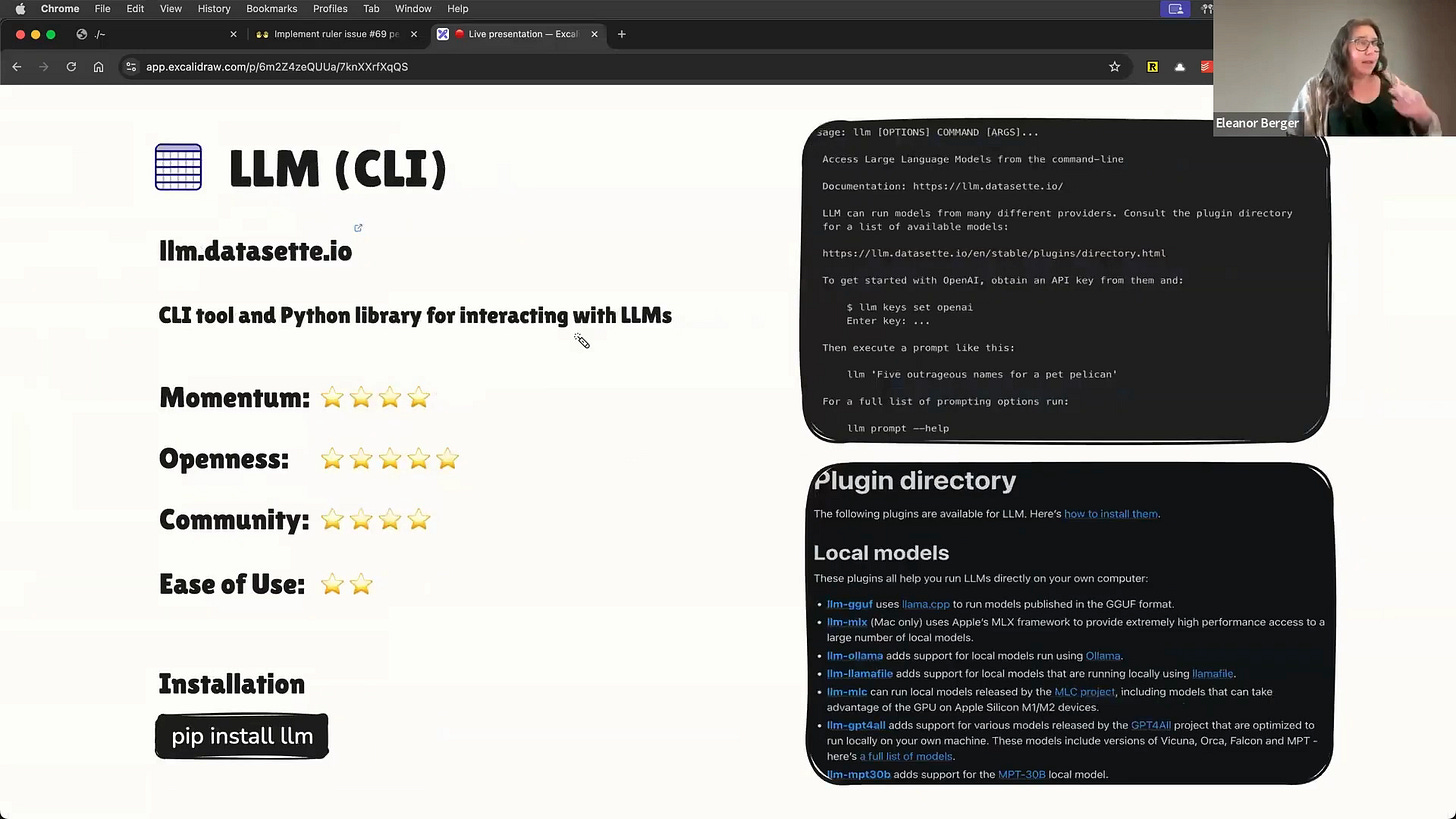
LLM Command Line Tool
Simon Willison's llm is not an agent, but it's an indispensable tool for any developer's toolbox [00:23:39]. It's a simple, versatile command-line utility for interacting with large language models. It's perfect for quick checks, small scripts, or integrating LLM calls into CI/CD pipelines like GitHub Actions [00:24:27].
LLM Tool Demonstration
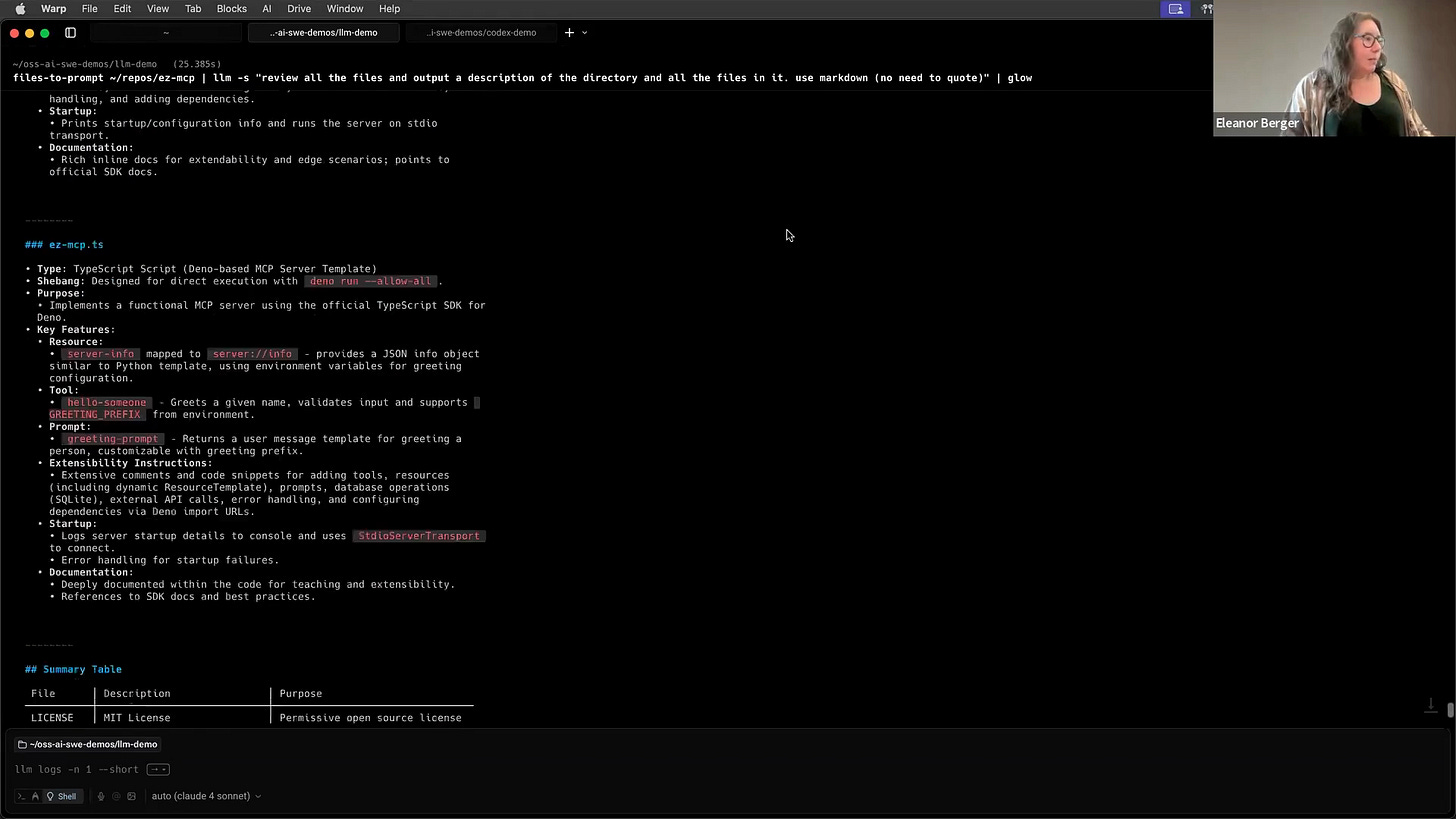
Here's a quick demo. I'm using a companion tool called files-to-prompt to concatenate all the files in a directory, and then piping that content into llm.
files-to-prompt . | llm -s "review all the files and output a description of everything and use markdown" | glowI provide a system prompt asking it to review the files and generate a markdown description. The output is then piped into glow for nice formatting in the terminal [00:25:18]. Behind the scenes, it makes a single API call to GPT-4.1 with the giant context and returns a clean, structured analysis of my project directory. It's incredibly useful for these kinds of ad-hoc tasks.
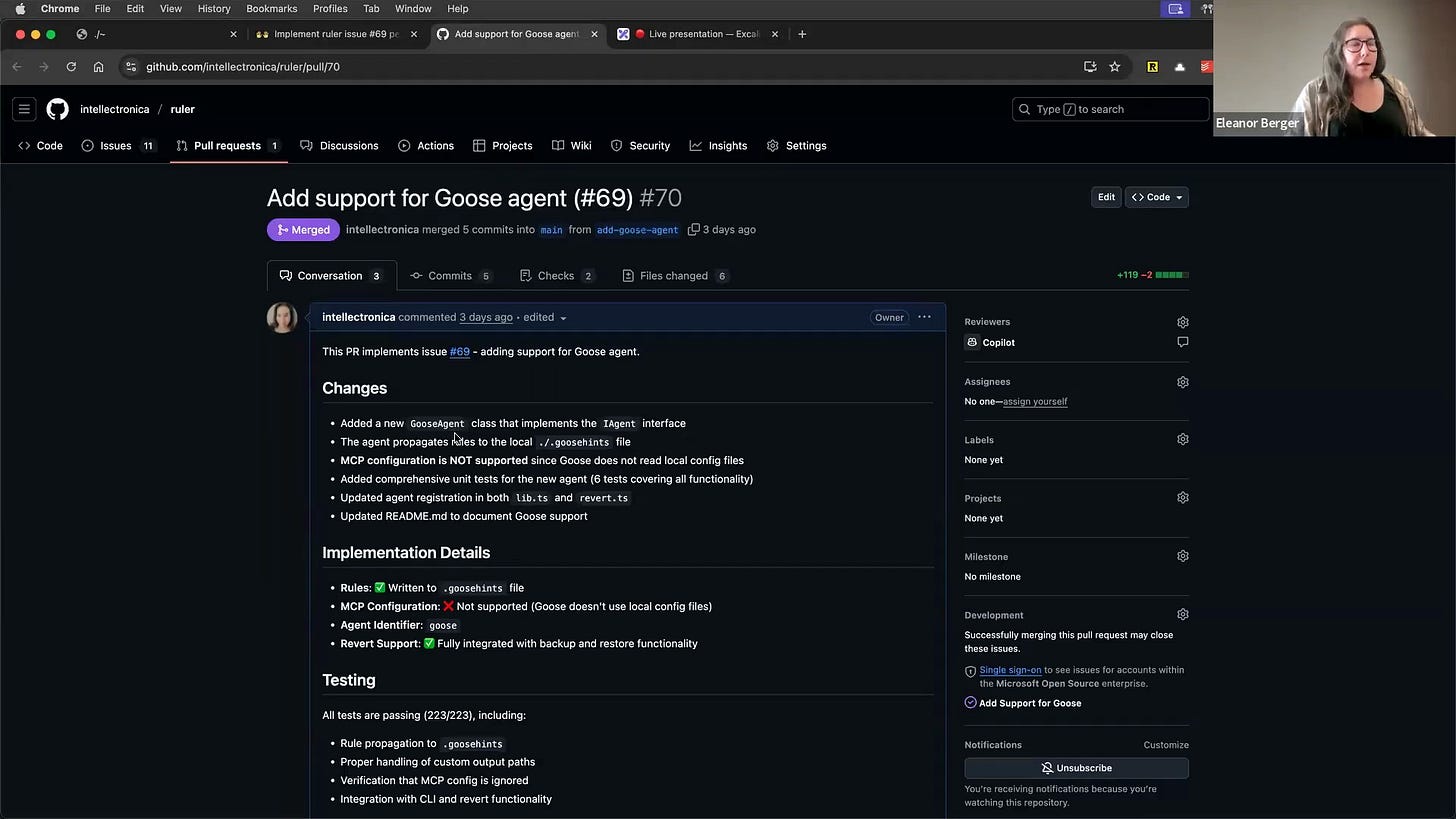
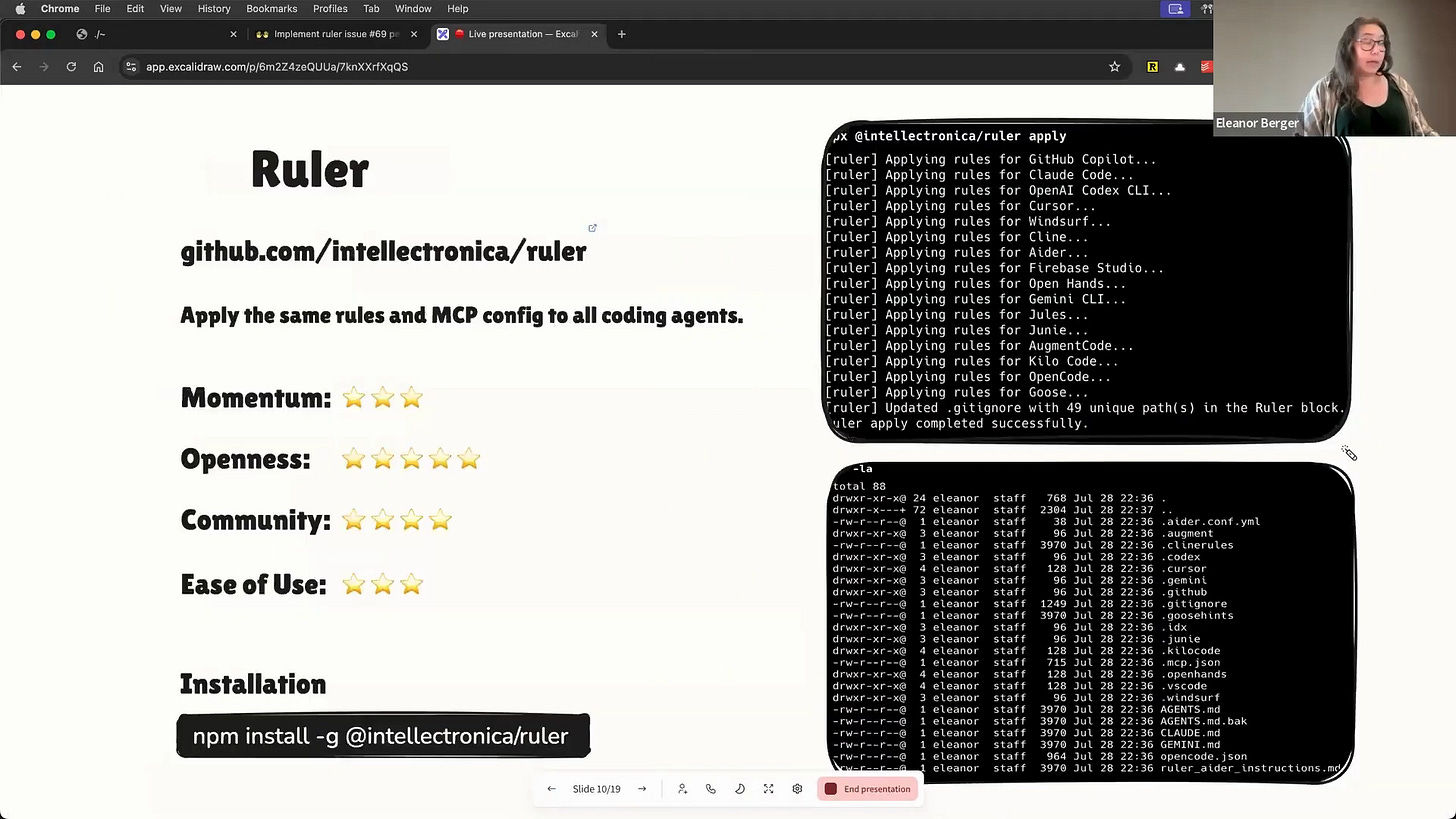
Ruler - Configuration Management
This is a bit of a shameless plug, as ruler is a tool I'm currently writing [00:26:24]. As I started working with all these different agents, I realized there was no good way to manage their configurations—the custom instructions, tool settings, etc.—especially for a team working on a single codebase [00:26:36].
So, I built ruler. It allows you to define your ideal configuration in one central place and then apply it to all the different agents you use. It's a simple tool that solves a real headache. I'm also proud to say it's the one project I've built entirely using AI coding assistants [00:27:12].
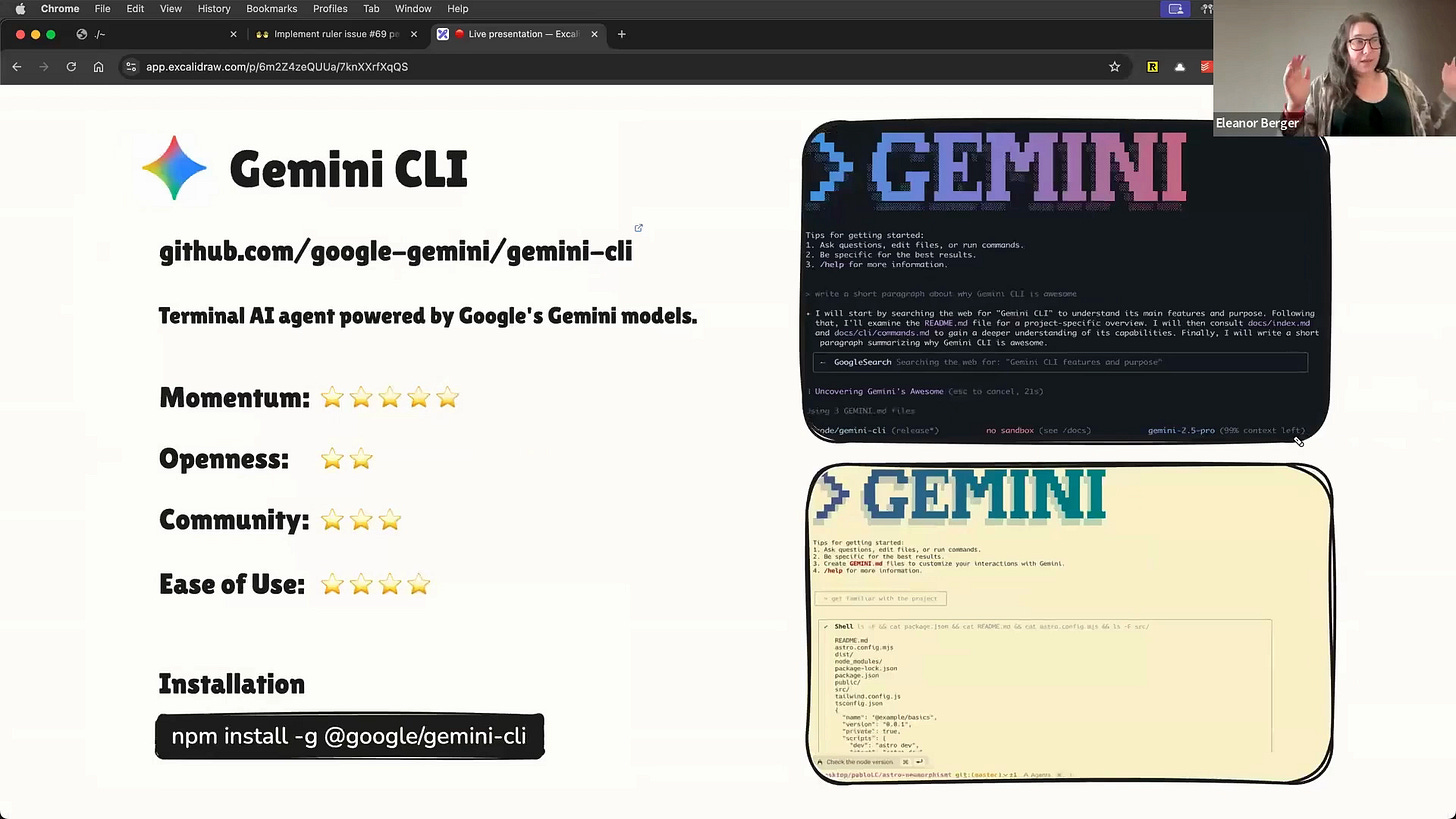
Other Notable Open Source Tools
The ecosystem is huge, and there are many other great tools worth your attention [00:28:27]: including Gemini CLI, opencode, Cline, and Goose.
The Future of Open Source AI Tools
Where is all of this heading? This is speculation, of course, but here's what I hope and expect to see [00:33:54]:
Open Source Tooling being adopted and surpassing proprietary models
Historically Open Source is dominant in other technical domains (linux, cryptography, etc.)
Q&A and Final Thoughts
We ended with a great Q&A session. A key theme was that while these tools are incredibly powerful, they are not magic. You, the developer, are still responsible for the quality of the final product [00:51:09].
Whether you're comparing two PRs generated by different agents or reviewing a single one, your expertise and taste are crucial. Use these tools to explore code, understand different approaches, and automate tedious work, but always remain in the loop to guide the process and ensure the final output meets your standards for quality, security, and maintainability [00:48:54].
Thank you for joining me on this tour. The world of open source AI-assisted development is moving at an incredible pace, and it's a fantastic time to jump in, experiment, and learn.
If you're interested in diving deeper, check out our course at AI Assisted Coding. Subscribe for more free content, tool reviews, and talks! [00:38:09]