Agentic Coding Workflows with Qoder CLI and Quest Mode
Lightning Talk with Hang Yu, Product Lead for Qoder @ Alibaba
Hang Yu, product lead at Qoder, presented a comprehensive vision for agentic coding that moves beyond simple code completion toward full task autonomy. His session traced the evolution from AI-assisted workflows to autonomous agents that work independently while developers focus on other tasks. The demonstration showcased two key capabilities — Quest mode for delegating complete tasks and a CLI for terminal-first developers — both running on the same underlying platform.
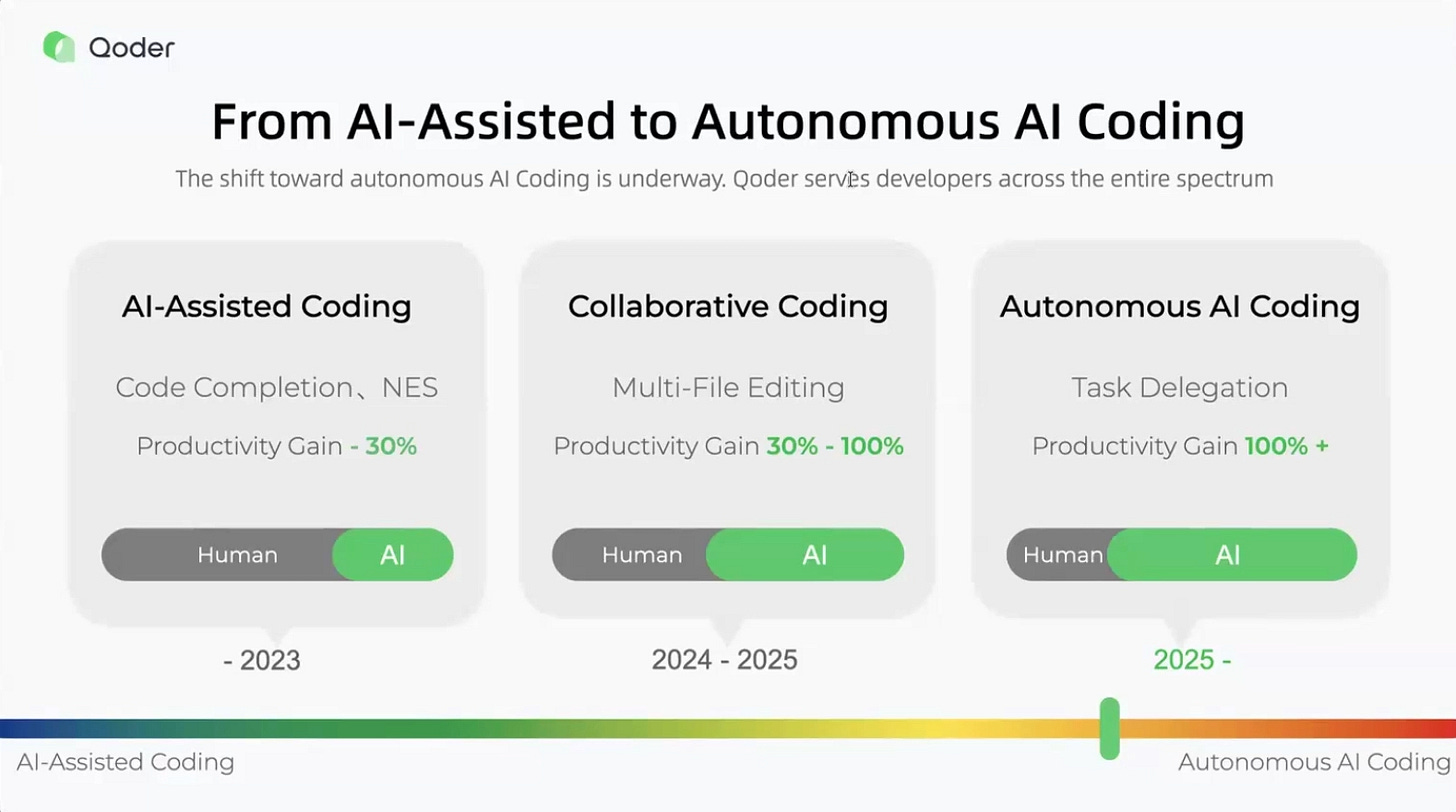
The Three-Stage Evolution
Yu structured AI coding into three distinct phases, each representing a fundamental shift in the human-AI relationship.
Stage One: AI-Assisted Coding arrived around 2022 with tools like early GitHub Copilot. The capability centered on code completion and next-line suggestions — ”auto-complete on steroids,” as Yu described it. Productivity gains reached approximately 30%, but developers remained in the driver’s seat for every decision. “You can’t walk away,” Yu noted. “You have to stay in the driver’s seat the whole time.”
Stage Two: Collaborative Coding emerged in 2024-2025, enabling multi-file editing and complex refactoring. The interaction resembles pair programming with an intelligent colleague. Yu illustrated: “You might say, ‘I need to refactor this module to support multi-database,’ and then AI says, ‘Okay, I see three ways to do this, and let me show you how.’” Productivity gains range from 30% to 100%, with AI handling heavy lifting while humans provide guidance. Tools like Qoder and Cursor operate in this space.
Stage Three: Autonomous AI Coding represents 2025 and beyond. The defining characteristic is task delegation: “You say, ‘There’s a GitHub issue. Go fix it. Let me know when it’s done.’ And AI just goes off and does it, independently, in the background.” Productivity exceeds 100% because developers delegate entire tasks. The key word is asynchronous — developers manage rather than supervise. As Yu’s team articulated: “Quest mode is about human being the leader and agents, AI doing the work.”
Yu emphasized that not every task requires autonomy. “Sometimes we want assistance, sometimes we want collaboration, but when we can hand off something and trust it gets done, that changes everything.”
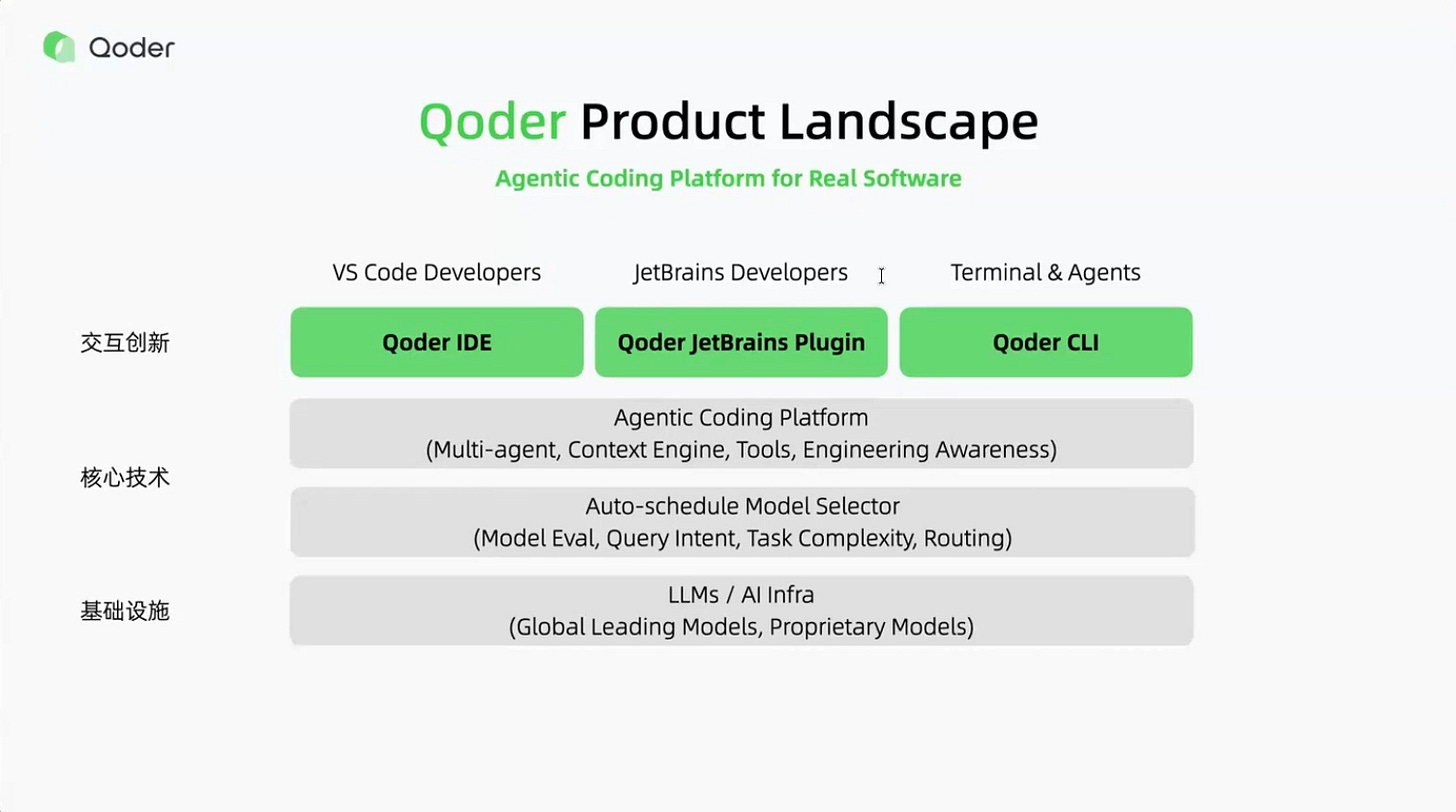
Platform Philosophy
Qoder’s architecture distinguishes itself from typical IDE-centric tools. Rather than building separate products for different interfaces, Qoder operates as a unified platform. “At the bottom, you have the brain, the intelligence, the models, the agents,” Yu explained. “And at the top, you have the interface.” When the core intelligence improves, every interface — VS Code, terminal, JetBrains, Vim — benefits simultaneously.
This approach extends to model selection. Unlike tools offering dropdown menus with 40 model choices, Qoder auto-selects optimal models based on task requirements. “Developers end up becoming model selectors instead of focusing on what they are trying to build,” Yu observed. The same principle applies to context management — Qoder handles file inclusion and token optimization automatically.
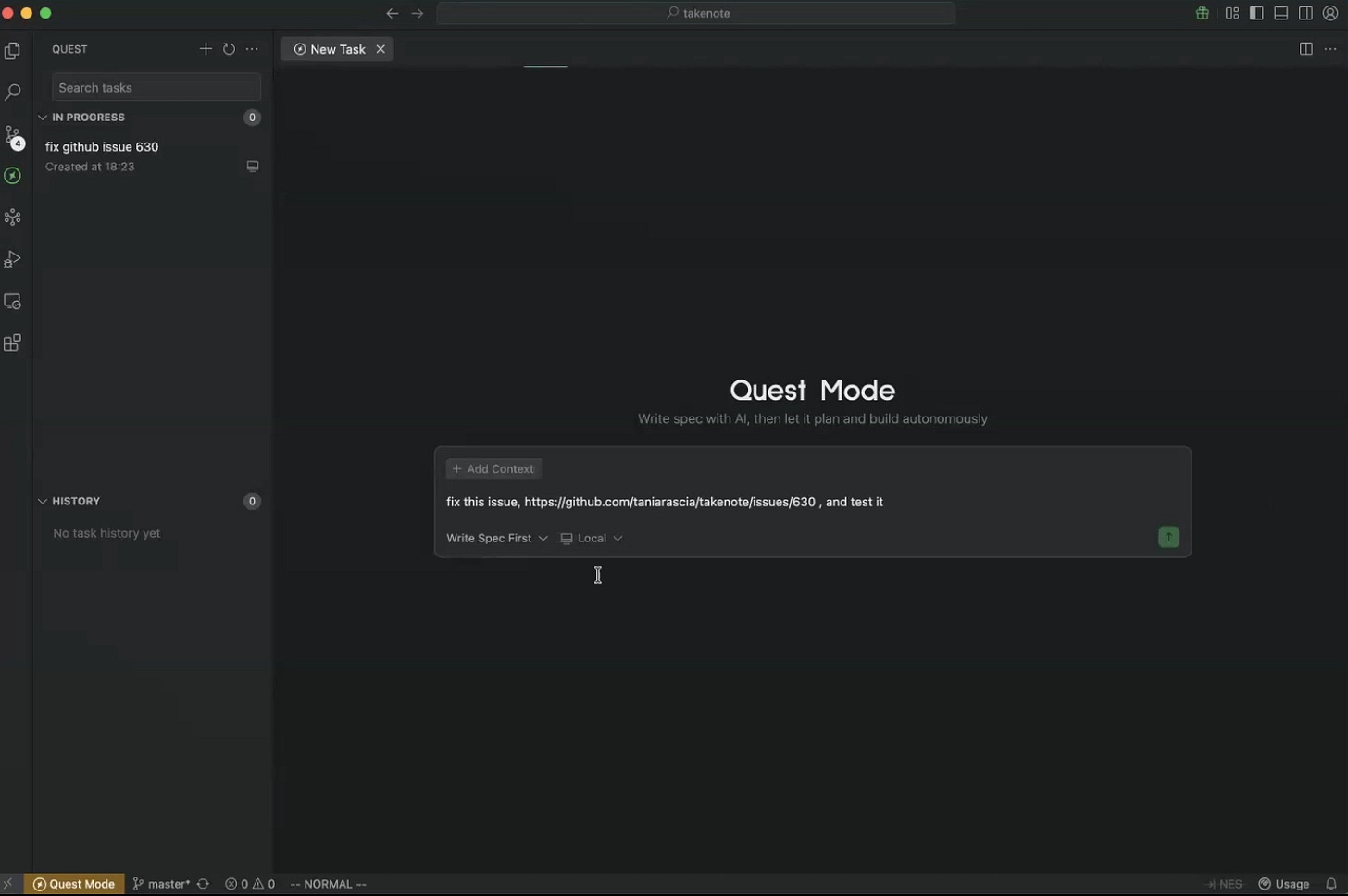
Quest Mode: Autonomous Task Delegation
Yu demonstrated Quest mode using TakeNote, a real open-source note-taking app with 7,100 GitHub stars. The repository had an open issue regarding npm installation failures related to node-sass and node-gyp dependencies.
After cloning the repository and confirming the installation error locally, Yu delegated the entire issue to Quest. The agent explored the codebase, analyzed the problem, and generated a detailed specification covering scope validation, testing strategy, production build verification, and rollback plans. Yu approved the plan, and Quest began autonomous implementation.
The critical advantage: “I don’t need to supervise. I can go work on something else.” Quest operates in the background, either locally or in cloud sandboxes that don’t require the developer’s laptop to remain active. For the demonstration, Yu ran it locally for speed but noted cloud execution provides true asynchronous operation.
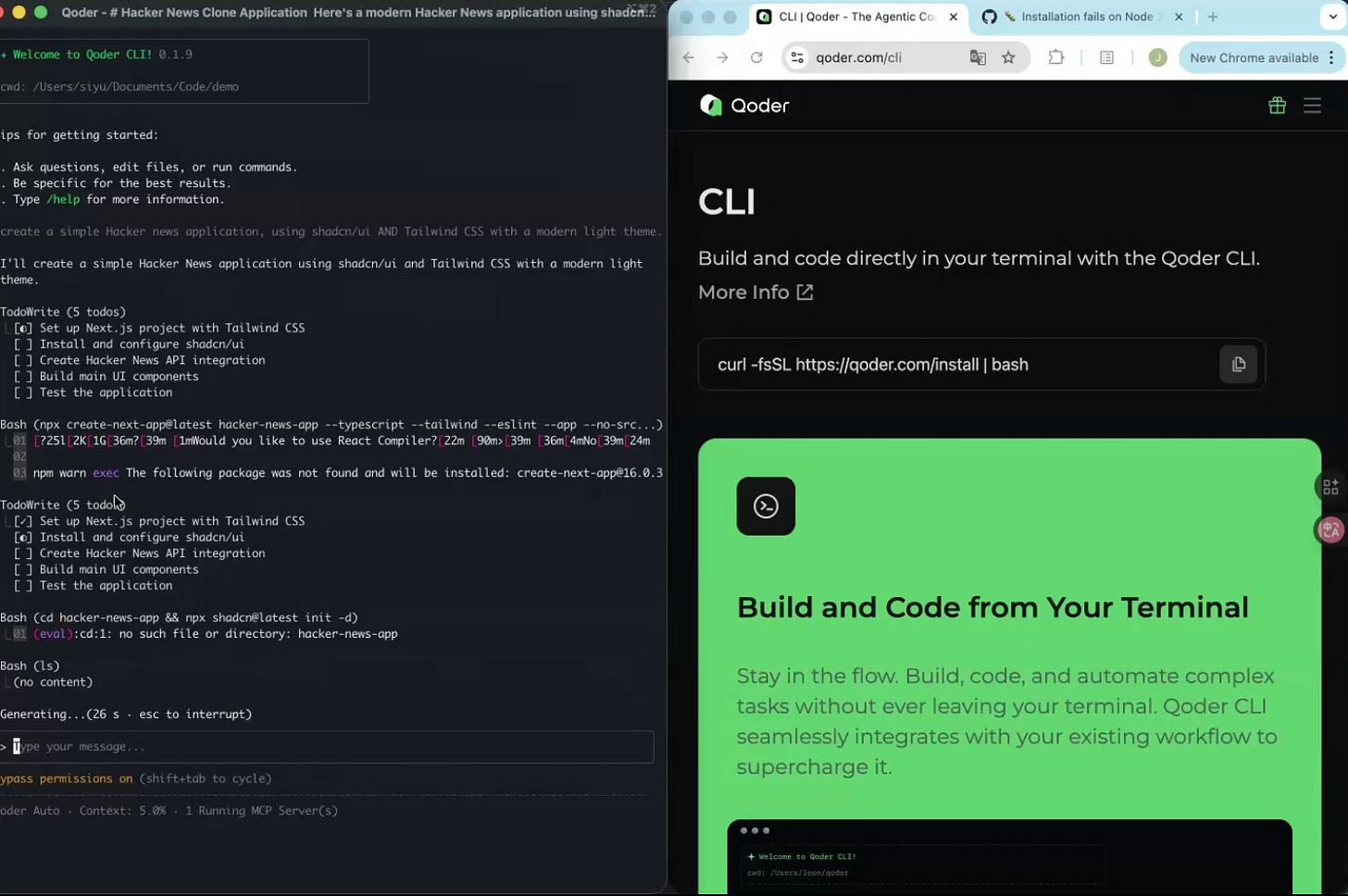
CLI: Terminal-First Development
While Quest worked autonomously, Yu switched to Qoder’s command-line interface to build a Hacker News reader app from scratch. The prompt was straightforward: “Create a simple Hacker News application, using Shad CN, UI, and Tailwind CSS and run it live.”
The CLI generated a todo list covering project setup, dependency installation, component creation, and API integration with Hacker News. Yu didn’t write code�he described requirements and the AI built the application. When port 3000 was occupied, he simply noted the issue; the CLI switched ports automatically.
After resolving two bugs through brief back-and-forth exchanges, the app launched successfully. Rather than manually testing in a browser, Yu leveraged MCP (Model Context Protocol) tools integrated into the CLI. “Test the app using MCP tools,” he instructed. Qoder CLI launched Chrome via DevTools MCP, navigated to the application, verified story loading, and clicked through to confirm links functioned correctly.
The entire process — building, debugging, and automated testing — took approximately 5-10 minutes without writing a single line of code manually.
Quest Results
Returning to Quest mode, Yu found the autonomous agent had completed the TakeNote issue. The agent had updated dependencies, cleaned installed packages, tested both development and production builds, ran unit tests, and verified application functionality. Running npm install again confirmed the bug was resolved.
Yu noted he would still review changes before merging, but “the heavy lifting is done, and I got to work on something else in the meantime.” This exemplifies the delegate-and-walk-away paradigm Quest enables.
Technical Insights from Q&A
When asked about model routing, Yu clarified that Qoder uses “globally optimal models” selected automatically based on task characteristics. “Machine selection is way better than human selection,” he argued, eliminating cognitive overhead that turns developers into configuration managers rather than builders.
For remote execution, Quest accesses GitHub repositories directly after obtaining permissions. Users can customize environments through Dockerfiles or configuration scripts that define the sandbox environment for code execution and testing.
Conclusion
Qoder positions itself across the full spectrum from assistance to autonomy, with particular emphasis on pushing toward independent agent operation. Quest mode targets complete task delegation with asynchronous execution, while the CLI meets terminal-first developers where they work, integrating AI into scripts, automation, and infrastructure tasks. Both operate on the same underlying intelligence platform, demonstrating Qoder’s commitment to adapting AI to developer workflows rather than forcing workflow changes to accommodate AI tools.